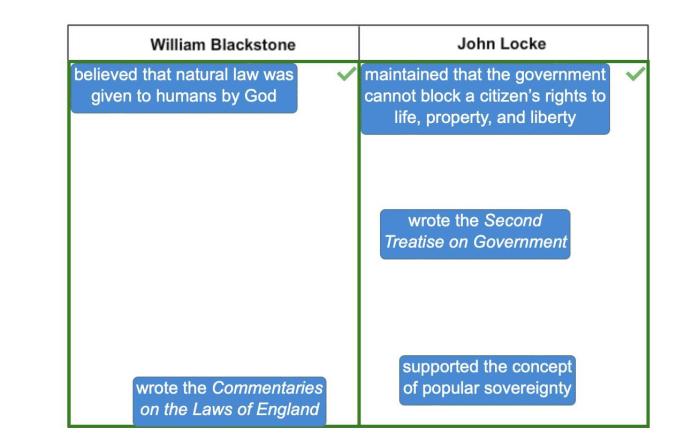
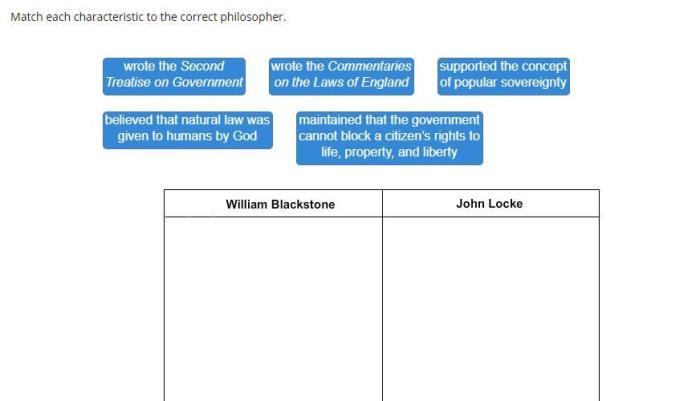
Match the ideas with the correct enlightenment philosopher embarks on an enlightening odyssey, delving into the profound minds that shaped the Enlightenment era. These intellectual luminaries ignited a revolution of reason, challenging traditional dogma and paving the way for modern thought.
Their ideas continue to resonate today, inspiring us to question, explore, and embrace the power of human reason.
From the rationalism of René Descartes to the empiricism of John Locke, from the social contract theories of Jean-Jacques Rousseau to the separation of powers advocated by Montesquieu, this guide unravels the tapestry of Enlightenment thought, illuminating the connections between philosophers and their groundbreaking ideas.
Philosophers and Their Ideas: Match The Ideas With The Correct Enlightenment Philosopher
The Enlightenment was a period of intellectual and philosophical change that took place in Europe during the 18th century. This period was characterized by a focus on reason, science, and the individual. Some of the most important philosophers of the Enlightenment include John Locke, Voltaire, Jean-Jacques Rousseau, and Immanuel Kant.
John Locke
John Locke (1632-1704) was an English philosopher who is considered one of the founders of modern liberalism. Locke believed that all people are born with natural rights, including the right to life, liberty, and property. He also argued that the government should be based on the consent of the governed.
Voltaire, Match the ideas with the correct enlightenment philosopher
Voltaire (1694-1778) was a French philosopher who is best known for his wit and his criticism of the Catholic Church. Voltaire believed that reason and tolerance were essential for a just and enlightened society.
Jean-Jacques Rousseau
Jean-Jacques Rousseau (1712-1778) was a Swiss philosopher who is best known for his work on social contract theory. Rousseau believed that the state of nature was a state of equality and freedom, and that the social contract was a way for people to protect their natural rights.
Immanuel Kant
Immanuel Kant (1724-1804) was a German philosopher who is considered one of the most important thinkers in the history of Western philosophy. Kant believed that reason was the source of all knowledge, and that the moral law was universal and binding on all people.
FAQ Overview
Who is considered the father of modern philosophy?
René Descartes
What is the central idea of empiricism?
All knowledge is derived from experience
Who proposed the theory of the social contract?
Jean-Jacques Rousseau