As worksheet development of atomic theory takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with academic rigor and authoritative tone, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original. Delving into the rich tapestry of atomic theory, we embark on a journey that unravels the fundamental concepts, historical milestones, and cutting-edge advancements that have shaped our understanding of the microscopic realm.
Worksheet development of atomic theory provides a structured and engaging approach to mastering this complex subject. Through interactive exercises, students can actively engage with the key principles, reinforce their understanding, and develop critical thinking skills. This comprehensive guide will equip educators and learners alike with the necessary tools and resources to create effective and impactful worksheets that foster a deep comprehension of atomic theory.
History of Atomic Theory Development: Worksheet Development Of Atomic Theory
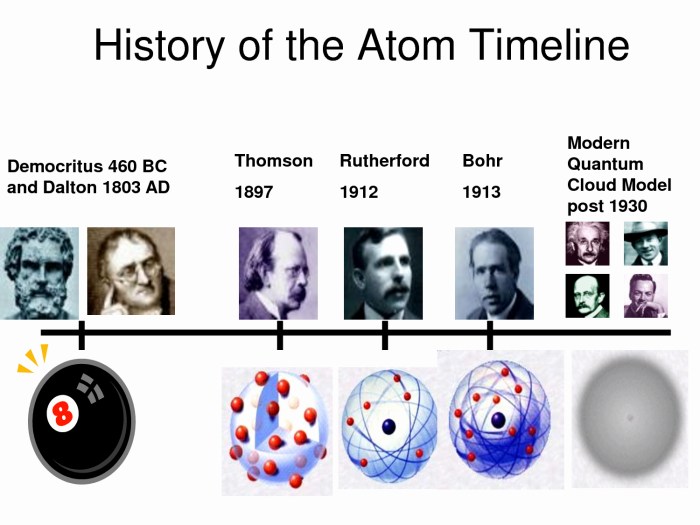
The development of atomic theory has been a gradual process, with many scientists contributing to our understanding of the atom. The key scientists and their contributions include:
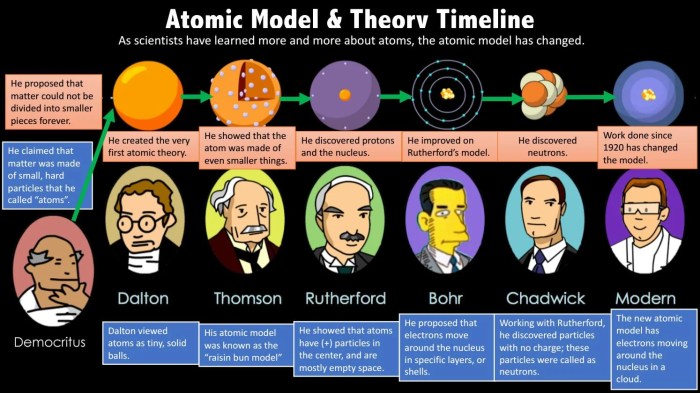
- John Dalton (1803): Proposed the first atomic theory, stating that matter is composed of indivisible particles called atoms.
- J.J. Thomson (1897): Discovered the electron and proposed the “plum pudding” model of the atom.
- Ernest Rutherford (1911): Conducted the gold foil experiment, which led to the discovery of the atomic nucleus.
- Niels Bohr (1913): Proposed the Bohr model of the atom, which introduced the concept of energy levels and electron orbits.
- Erwin Schrödinger (1926): Developed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which uses wave functions to describe electron behavior.
The evolution of atomic models over time has been driven by experimental evidence and theoretical advancements. Each new model has provided a more accurate and comprehensive description of the atom, leading to a deeper understanding of its structure and properties.
Major discoveries and breakthroughs in atomic theory include:
- 1803: Dalton’s atomic theory
- 1897: Thomson’s discovery of the electron
- 1911: Rutherford’s discovery of the atomic nucleus
- 1913: Bohr’s model of the atom
- 1926: Schrödinger’s quantum mechanical model of the atom
Fundamental Concepts of Atomic Theory

Atomic theory is based on the following fundamental concepts:
- Atoms: Atoms are the basic building blocks of matter and are indivisible by chemical means.
- Elements: Elements are pure substances composed of only one type of atom.
- Isotopes: Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons.
The structure of an atom consists of a nucleus and electrons:
- Nucleus: The nucleus is the central part of the atom and contains protons and neutrons.
- Electrons: Electrons are negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus.
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of elements organized by their atomic number, which is the number of protons in the nucleus. The periodic table helps to predict the chemical properties of elements based on their atomic structure.
Applications of Atomic Theory
Atomic theory has numerous applications in various fields, including:
- Chemical reactions and bonding: Atomic theory helps to explain how atoms interact to form molecules and compounds.
- Materials science and nanotechnology: Atomic theory is used to understand the properties of materials and to design new materials with desired properties.
- Medicine: Atomic theory is used in medical imaging techniques, such as X-rays and MRI scans.
Modern Developments in Atomic Theory
Recent advancements in atomic theory include:
- Quantum mechanics: Quantum mechanics is used to understand the behavior of atoms and subatomic particles at the quantum level.
- Atomic orbitals: Atomic orbitals are mathematical functions that describe the probability of finding an electron in a specific region of space.
- Quantum computing: Quantum computing uses the principles of quantum mechanics to perform complex calculations.
User Queries
What are the key benefits of using worksheets in teaching atomic theory?
Worksheets provide a structured and interactive approach to learning, allowing students to actively engage with the material and reinforce their understanding through practice.
How can I incorporate different learning styles into worksheet development?
Consider using a variety of activities such as diagrams, simulations, problem-solving exercises, and open-ended questions to cater to diverse learning preferences.
What are some common misconceptions about atomic theory that can be addressed through worksheets?
Worksheets can help clarify misconceptions about the nature of atoms, the structure of the nucleus, and the role of electrons in chemical bonding.
