Cleft lip and cleft palate hesi case study – Cleft lip and cleft palate are birth defects that occur when the lip or palate does not form properly during pregnancy. These conditions can range in severity from a small notch in the lip to a complete separation of the lip or palate.
Cleft lip and cleft palate are relatively common, affecting approximately 1 in 700 live births.
This case study will provide an overview of the etiology, epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnostic evaluation, treatment, nursing management, and long-term outcomes of cleft lip and cleft palate. It will also discuss the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration in the care of patients with these conditions.
Etiology and Epidemiology
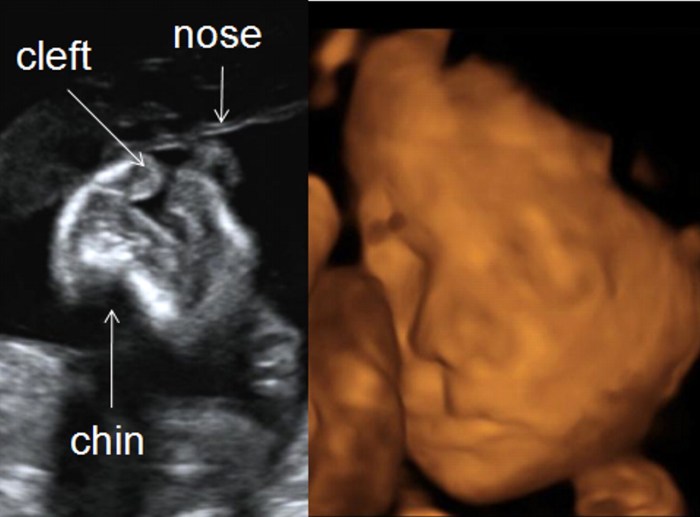
Cleft lip and palate (CLP) is a birth defect that occurs when the lip and/or palate do not fuse properly during pregnancy. The exact cause of CLP is unknown, but it is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
CLP is one of the most common birth defects, affecting approximately 1 in 700 live births. It is more common in certain populations, such as those of Asian and Native American descent.
Pathophysiology
The development of the lip and palate begins in the early stages of pregnancy. The lip forms from two prominences, called the medial and lateral nasal prominences, which fuse together in the midline. The palate forms from two shelves, called the palatal shelves, which grow down from the roof of the mouth and fuse together in the midline.
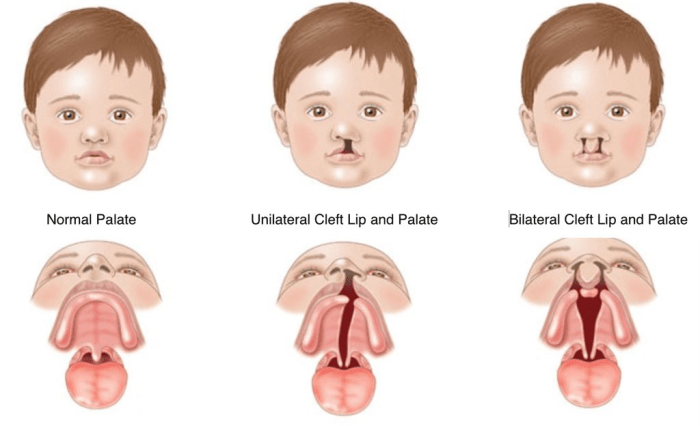
CLP can occur if the medial nasal prominences or the palatal shelves fail to fuse properly. This can result in a variety of different types of CLP, including:
- Cleft lip
- Cleft palate
- Cleft lip and palate
Clinical Presentation
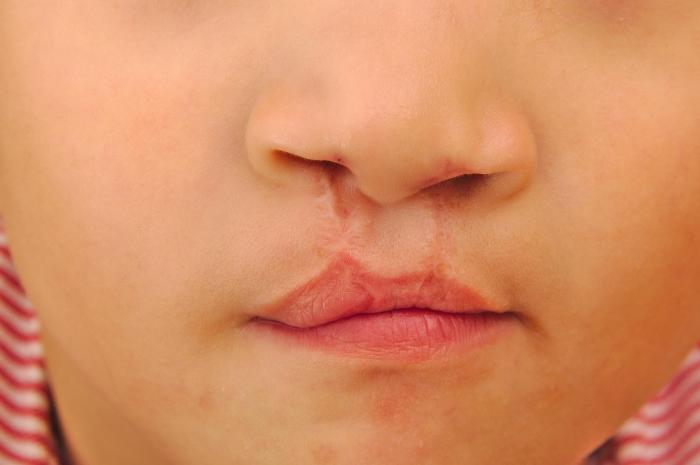
The clinical presentation of CLP can vary depending on the type and severity of the defect. Common features include:
- A cleft in the lip
- A cleft in the palate
- Difficulty feeding
- Speech problems
- Dental problems
- Hearing problems
CLP can also be associated with other birth defects, such as heart defects, kidney defects, and gastrointestinal defects.
Diagnostic Evaluation
CLP can be diagnosed prenatally through ultrasound. After birth, the diagnosis can be confirmed through a physical examination.
The physical examination should include an assessment of the lip, palate, and teeth. The examiner should also look for any other associated birth defects.
Treatment
The treatment for CLP is surgery. The goal of surgery is to close the cleft and restore normal function to the lip and palate.
The type of surgery that is performed will depend on the type and severity of the cleft. Common surgical techniques include:
| Surgical Technique | Timing | Expected Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Cleft lip repair | 3-6 months of age | Improved appearance and function of the lip |
| Cleft palate repair | 6-12 months of age | Improved speech and feeding |
Nursing Management
Nurses play an important role in the care of patients with CLP. Nursing interventions include:
- Providing preoperative and postoperative care
- Teaching parents how to care for their child with CLP
- Providing support to families
Nurses should also be aware of the potential long-term complications of CLP and be prepared to provide ongoing support to patients and their families.
Long-Term Outcomes: Cleft Lip And Cleft Palate Hesi Case Study

The long-term outcomes for patients with CLP depend on the type and severity of the defect and the quality of care they receive. With proper treatment, most patients with CLP can live full and productive lives.
Potential long-term complications of CLP include:
- Speech problems
- Dental problems
- Hearing problems
- Social and emotional problems
Data show that patients with CLP have a higher risk of developing mental health problems, such as anxiety and depression. They may also be more likely to experience bullying and social isolation.
FAQ Compilation
What are the causes of cleft lip and cleft palate?
The exact causes of cleft lip and cleft palate are unknown, but they are thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
How are cleft lip and cleft palate diagnosed?
Cleft lip and cleft palate can be diagnosed prenatally through ultrasound or after birth through a physical examination.
What are the treatment options for cleft lip and cleft palate?
The treatment for cleft lip and cleft palate typically involves surgery to repair the lip and palate. Surgery is usually performed in stages, with the first stage typically occurring within the first few months of life.
What are the long-term outcomes for individuals with cleft lip and cleft palate?
With early intervention and appropriate treatment, most individuals with cleft lip and cleft palate can live full and productive lives. However, some individuals may experience long-term complications, such as speech problems, dental problems, or hearing loss.