An introduction to cladograms and trees answer key sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with gaya akademik dengan tone otoritatif and brimming with originality from the outset.
These diagrams, employed extensively in scientific research, provide invaluable insights into the evolutionary relationships among organisms, revealing the intricate tapestry of life’s history.
Cladograms and trees, indispensable tools in the fields of biology and systematics, offer a visual representation of evolutionary relationships. They depict the branching patterns of lineages, providing a framework for understanding the diversification of species over time. This guide delves into the intricacies of these diagrams, exploring their components, construction, and interpretation, empowering readers to decipher the evolutionary narratives they convey.
1. Introduction to Cladograms and Trees
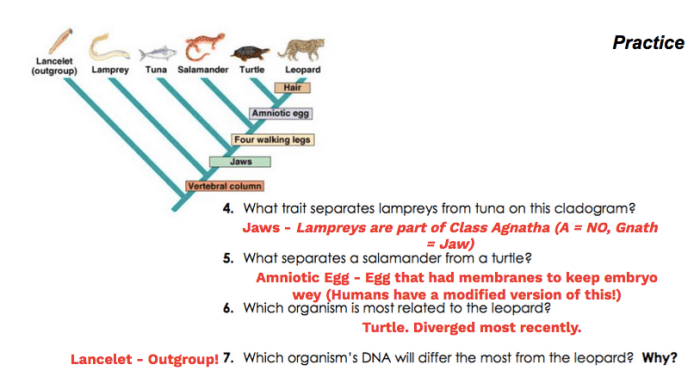
Cladograms and phylogenetic trees are graphical representations of evolutionary relationships among organisms. They depict the branching patterns of common ancestors and their descendants, providing insights into the evolutionary history of species.
These diagrams serve as valuable tools for taxonomists, evolutionary biologists, and ecologists, enabling them to:
- Classify and organize species based on their shared characteristics
- Infer the ancestral relationships between different groups
- Study the patterns and processes of evolution
Cladograms and trees have been extensively used in various scientific fields, including systematics, biogeography, and conservation biology.
2. Components of Cladograms and Trees
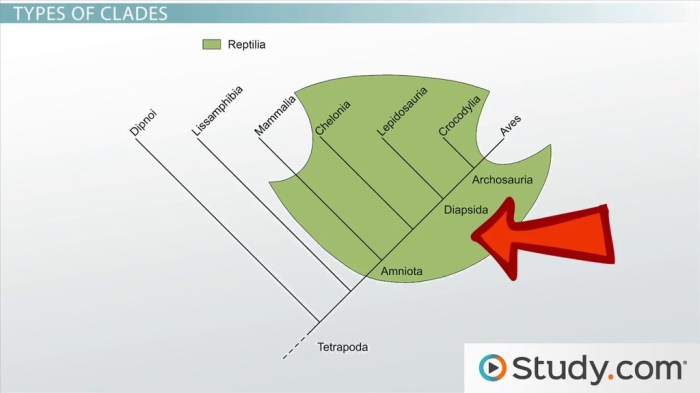
Key Components
- Nodes:Represent branching points where lineages diverge
- Branches:Connect nodes and represent evolutionary lineages
- Terminals:Represent individual species or operational taxonomic units
Branch Lengths
In some cladograms and trees, branch lengths may be proportional to the amount of evolutionary change or time that has occurred along that branch.
Root Nodes
The root node represents the common ancestor from which all other taxa in the diagram are descended.
3. Constructing Cladograms and Trees
Steps for Construction
- Gather data on the characteristics of the organisms being studied
- Choose a method for constructing the diagram, such as parsimony or maximum likelihood
- Analyze the data using appropriate software tools
- Interpret the resulting cladogram or tree
Methods for Construction
Common methods for constructing cladograms and trees include:
- Parsimony: Assumes that the simplest explanation for the observed data is the most likely
- Maximum likelihood: Estimates the probability of a tree given the observed data
Software Tools
Various software tools are available for constructing cladograms and trees, such as PAUP*, MEGA, and BEAST.
4. Interpreting Cladograms and Trees: An Introduction To Cladograms And Trees Answer Key
Inferring Evolutionary Relationships
Cladograms and trees can be used to infer evolutionary relationships among organisms by examining the branching patterns and the placement of taxa within the diagram.
Monophyletic, Paraphyletic, and Polyphyletic Groups
- Monophyletic:A group that includes a common ancestor and all of its descendants
- Paraphyletic:A group that includes a common ancestor but excludes some of its descendants
- Polyphyletic:A group that does not include a common ancestor
Examples of Interpretation
Cladograms and trees have been used to understand the evolutionary relationships of various organisms, including:
- The phylogenetic relationships among primates
- The evolutionary history of birds
- The diversification of flowering plants
5. Limitations and Applications
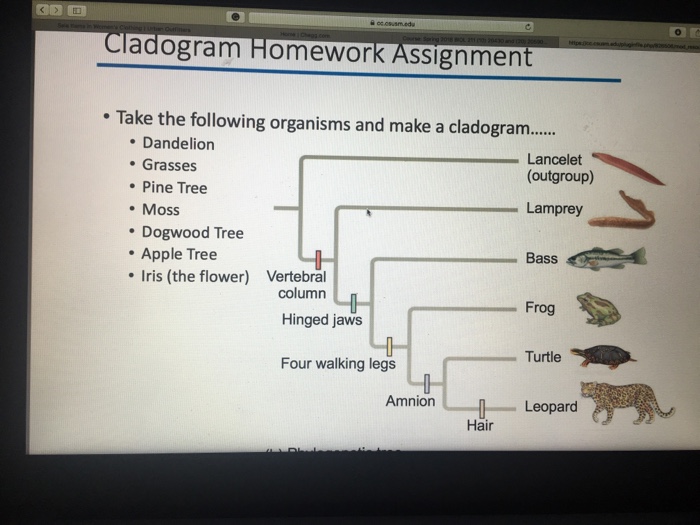
Limitations
Cladograms and trees are simplified representations of evolutionary history and have limitations:
- They may not accurately reflect the true branching patterns due to factors such as incomplete data or convergent evolution
- They assume a strictly bifurcating pattern of evolution, which may not always be the case
Applications, An introduction to cladograms and trees answer key
Despite their limitations, cladograms and trees are valuable tools in various fields:
- Taxonomy:Classifying and organizing species
- Systematics:Studying the evolutionary relationships among organisms
- Biogeography:Understanding the distribution of species across geographic regions
- Conservation:Identifying and prioritizing species for conservation efforts
FAQ Compilation
What is the purpose of a cladogram?
A cladogram is a diagram that represents the evolutionary relationships among a group of organisms. It shows the branching patterns of lineages, indicating the common ancestors and the order in which different groups diverged.
How are cladograms constructed?
Cladograms are constructed using a variety of methods, including parsimony and maximum likelihood. These methods analyze shared characteristics among organisms to infer their evolutionary relationships.
What is the difference between a cladogram and a phylogenetic tree?
A cladogram is a diagram that shows the branching patterns of lineages, while a phylogenetic tree is a diagram that shows the branching patterns of lineages and also includes branch lengths. Branch lengths represent the amount of evolutionary change that has occurred along a particular lineage.