Embarking on a journey through the origins of American government, this comprehensive guide delves into the foundational principles and pivotal events that shaped the nation’s political landscape. Chapter 2 Origins of American Government Worksheet Answers unravels the intricacies of the American government’s genesis, providing a roadmap to understanding its evolution and enduring legacy.
From the seeds of revolution sown in the Declaration of Independence to the intricate framework established by the Constitution, this exploration unveils the ideas, documents, and individuals that laid the groundwork for a government “of the people, by the people, for the people.”
American Government Origins: Chapter 2 Origins Of American Government Worksheet Answers

The origins of American government can be traced back to the English colonial experience and the ideas of the Enlightenment. The American colonists were influenced by the English tradition of common law and representative government, as well as by the Enlightenment ideals of natural rights, limited government, and popular sovereignty.
The key events and documents that shaped the American government include the Declaration of Independence (1776), the Articles of Confederation (1781), and the Constitution (1789). The Declaration of Independence declared the American colonies’ independence from Great Britain and asserted the principles of natural rights, limited government, and popular sovereignty.
The Articles of Confederation established a loose confederation of states with a weak central government. The Constitution replaced the Articles of Confederation and established a stronger central government with three branches: the legislative, executive, and judicial.
Timeline of Major Events in the Development of American Government
- 1607: Founding of Jamestown, the first permanent English settlement in North America.
- 1776: Declaration of Independence.
- 1781: Articles of Confederation.
- 1789: Constitution.
The Declaration of Independence
The Declaration of Independence is one of the most important documents in American history. It was adopted by the Continental Congress on July 4, 1776, and declared the American colonies’ independence from Great Britain. The Declaration of Independence asserted the principles of natural rights, limited government, and popular sovereignty.
The Declaration of Independence had a profound impact on the American Revolution. It provided a justification for the colonists’ rebellion against British rule and inspired them to fight for their independence. The Declaration of Independence also influenced the development of other revolutions around the world, including the French Revolution.
Key Ideas and Principles Expressed in the Declaration of Independence, Chapter 2 origins of american government worksheet answers
- All men are created equal.
- All men are endowed with certain unalienable rights, including life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness.
- Governments are instituted to protect the rights of the people.
- Governments derive their just powers from the consent of the governed.
The Constitution
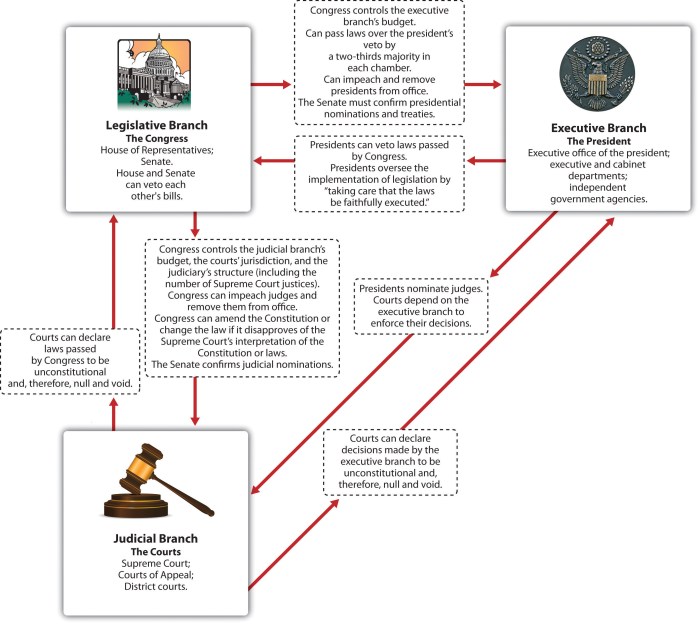
The Constitution is the supreme law of the United States. It was adopted by the Constitutional Convention in 1787 and ratified by the states in 1789. The Constitution established a strong central government with three branches: the legislative, executive, and judicial.
The Constitution has been amended 27 times since its adoption. The most important amendments include the Bill of Rights (1791), which guarantees individual liberties, and the 14th Amendment (1868), which guarantees equal protection under the law.
Structure and Principles of the Constitution
- The Constitution establishes a strong central government with three branches: the legislative, executive, and judicial.
- The legislative branch is composed of the Senate and the House of Representatives.
- The executive branch is headed by the President.
- The judicial branch is composed of the Supreme Court and lower federal courts.
Federalism
Federalism is a system of government in which power is divided between a central government and regional governments. The United States is a federal republic, which means that it is a federation of states with a strong central government.
Federalism has a number of advantages. It allows for a diversity of laws and policies to meet the needs of different regions. It also helps to protect individual liberties by preventing the central government from becoming too powerful.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Federalism
Advantages
- Allows for a diversity of laws and policies to meet the needs of different regions.
- Helps to protect individual liberties by preventing the central government from becoming too powerful.
Disadvantages
- Can lead to conflict between the central government and regional governments.
- Can make it difficult to pass national laws and policies.
The Bill of Rights
The Bill of Rights is the first ten amendments to the Constitution. It was adopted in 1791 and guarantees individual liberties, such as freedom of speech, religion, and the press. The Bill of Rights is one of the most important documents in American history and has been cited as a model for other constitutions around the world.
The Bill of Rights has had a profound impact on American law and society. It has protected individual liberties from government encroachment and has helped to ensure that the United States remains a free and democratic society.
Key Rights and Freedoms Guaranteed by the Bill of Rights
- Freedom of speech
- Freedom of religion
- Freedom of the press
- Right to assemble
- Right to bear arms
The American Revolution
The American Revolution was a war of independence fought between Great Britain and the American colonies from 1775 to 1783. The American colonists were fighting for their independence from British rule. The American Revolution was successful and resulted in the creation of the United States of America.
The American Revolution had a profound impact on the United States and the world. It was the first successful colonial rebellion against a European power. The American Revolution also inspired other revolutions around the world, including the French Revolution.
Causes and Consequences of the American Revolution
Causes
- British taxation policies
- British restrictions on trade
- British military presence in the colonies
Consequences
- Creation of the United States of America
- Inspiration for other revolutions around the world
- Development of a new form of government: the federal republic
FAQ Corner
What is the significance of the Declaration of Independence?
The Declaration of Independence proclaimed the American colonies’ independence from British rule and articulated the fundamental principles of self-governance, individual rights, and popular sovereignty.
How did the Constitution establish a framework for American government?
The Constitution established a federal system of government with three branches (executive, legislative, and judicial) and a system of checks and balances to prevent any one branch from becoming too powerful.
What are the key principles of federalism?
Federalism divides power between a central government and state governments, allowing for both national unity and local autonomy.